Publications
“Figure 1 summarizes the distribution of scores across countries for the manufacturing dataset, with the highlighted colored boxes indicating the interquartile range of scores and the grey whiskers covering the distribution of scores beyond the 25th and 75th percentile for each country. The marker indicates the median score for each country and the countries are ordered relative to their median scores by continent. There is substantial variation across and within countries in the overall management score alone. Work with census data or survey data from statistical agencies has the benefit of including a large number of observations and links to other performance data within their respective countries, though often have limited accessibility and cross-country comparability.”
This picture illustrates that lack of money is the most common reason that Black Females indicate for being unbanked, not fees or trust. This underscores the connection between wealth and financial inclusion, and the persistent and wide-ranging effects of wealth inequality.
This figure illustrates the lending behavior and drivers of for-profit, profit-maximizing MFIs that are monopolists, meaning they face no competitors in lending to their segment of customers. The solid line represents the deposit-taking marginal profit line and the dotted line represents the non-deposit-taking marginal profit line. One implication is that client-maximizing firms are more likely to not accept deposits. Adding to results around client-maximizing firms, we conclude that differences in financing affect the borrowers targeted, but different objective functions also influence both borrower targeting and the choice of financing and strengthens this relationship.
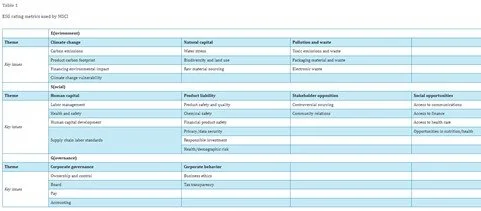
“When determining what issues are relevant for nonmarket strategy, practitioners can reference one of the many social responsibility indexes, to get a first look at how firm performance along these dimensions is measured. MSCI, for example, rates over 2800 firms’ environmental, social, and governance performance along specified metrics, which they share publicly on their website (MSCI, 2020). The top ten themes within these categories and the key issues within each theme are listed in Table 1.”
Researcher PRocess Model
We suggest researchers follow a triangulation approach to properly deal with selection issues, rather than defaulting to the Heckman method without a valid instrument.
Revisiting the world management survey in strategy: Applications to theory and replication
(with D. Scur)
in Strategy Science (2024)
Abstract: The academic field of strategy has a strong history of developing theories and frameworks to explain real-world phenomena, but a relatively younger empirical literature testing these theories. Partly due to the nature of questions in strategic management, scholars have often relied on collecting their own data or using specialized, and often expensive, proprietary data. This limits the possibility of replication exercises, which are a key step to refining and reinforcing the theories that are most supported in practice. To support this effort, we revisit the World Management Survey (WMS): a cross-country, cross-industry survey dataset with over 20,000 observations at the establishment-level that is collected through a rigorous and well-documented process and made free and accessible to researchers. While it is not without influence in the strategy literature, we propose it is underused and better exposure to this data’s offerings has the potential to add significant value to the field.
Suggested Citation: Scur, D., & Wolfolds, S. (2024). Revisiting the world management survey in strategy: Applications to theory and replication. Strategy Science, 9(1), 58-78.
Intersectionality and Financial Inclusion in the United States
(with V. Bogan)
In AEA Papers and Proceedings (2022)
Abstract: Recent estimates indicate approximately 8.4 million US households are unbanked with an additional 24.2 million US households classified as underbanked. We focus on intersectionality, specifically the intersection of race and gender, to better understand the probability of being unbanked and underbanked in the US. Additionally, we look at drivers of this financial exclusion. We find Black women are significantly more likely than Black men or any other group to be unbanked or to be underbanked. Further, we find limited wealth is more frequently cited by Black women as the main reason why they do not engage with the banking system.
Suggested Citation: Bogan, Vicki L., and Sarah E. Wolfolds. 2022. "Intersectionality and Financial Inclusion in the United States." AEA Papers and Proceedings, 112: 43-47.
segmenting Mixed Markets: a Model and Evidence from microfinance
In Business With a Conscience: A Research Companion (2022).
See here for the online appendix with proofs.
Abstract: Although there are an increasing number of contexts where organizations with distinct goals and approaches compete and coexist, the competitive dynamics between organizations with distinct business models have only recently become an area for theoretical and empirical analysis. Using the setting of microfinance, a mixed industry in which non-profits and for-profits directly compete, this chapter develops a formal analytical model investigating the objectives that organizations pursue to understand the resulting differences in business models. Specifically, this model allows me to explore the firm characteristics, focusing on objective functions and sources of financing, that determine the strategic choices they make, in terms of which customers to lend to. Allowing for the endogenous choice of sources of financing leads to the hypothesis that non-profits may focus on even lower income borrowers when they face more for-profit competitors, providing important insight into the future of these mixed industries and the role of purpose-driven organizations.
Suggested Citation: Wolfolds, S. (2022). In Business With a Conscience: A Research Companion. Ed. Joan Marques. Routledge: New York, 194-210.
Nonmarket strategy
(with A. Hugill)
In The Palgrave Encyclopedia of Interest Groups, Lobbying and Public Affairs (2022).
Abstract: The field of nonmarket strategy has expanded the range of issues managers consider when setting the strategic goals and implementation activities for firms. Nonmarket strategy examines the role social forces such as environmental concerns, social justice issues, and cultural norms, as well as governmental forces such as laws, regulatory bodies, and government engagement activities like lobbying play on business activities and industries generally. Based on the understanding developed during such an examination, businesses may choose to address such issues proactively with a nonmarket strategy, which is similar to and likely synergistic with their traditional market strategy, that details a plan for how that business engages with the nonmarket issue. Motivations for nonmarket strategy include both altruistic goals and performance goals.
Suggested Citation: Hugill A.R., Wolfolds S.E. (2021) Nonmarket Strategy. In: Harris P., Bitonti A., Fleisher C.S., Binderkrantz A.S. (eds) The Palgrave Encyclopedia of Interest Groups, Lobbying and Public Affairs. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-13895-0_204-1
Misaccounting for Endogeneity: The Peril of Relying on the Heckman Two-Step Method without a Valid Instrument
(with J. Siegel)
Strategic Management Journal (2019)
See my discussion of this paper at the Strategic Management Society’s Research Methods Doctoral Student & Jr Faculty Consortium in April 2021: https://youtu.be/g9a_0gTMebA.
Research Summary: Strategy research addresses endogeneity by incorporating econometric techniques, including Heckman's two-step method. The economics literature theorizes regarding optimal usage of Heckman's method, emphasizing the valid exclusion condition necessary in the first stage. However, our meta-analysis reveals that only 54 of 165 relevant papers published in the top strategy and organizational theory journals during 1995–2016 claim a valid exclusion restriction. Without this condition being met, our simulation shows that results using the Heckman method are often less reliable than OLS results. Even where Heckman is not possible, we recommend that other rigorous identification approaches be used. We illustrate our recommendation to use a triangulation of identification approaches by revisiting the classic global strategy question of the performance implications of cross-border market entry through greenfield or acquisition.
Suggested Citation: Wolfolds, S., Siegel, J. (2019). Misaccounting for Endogeneity: The Peril of Relying on the Heckman Two-Step Method without a Valid Instrument. Strategic Management Journal, 40(3): 432-462.
This table regresses Terminated on alternative control variables to address concerns that contracting environment is proxying for economic development. Specifically, we separately orthogonalize both the International Country Risk Guide’s Contract Viability and the Heritage Foundation’s Property Rights measures with both GDP per capita and total GDP and add them as controls.
TIED UP AND SHOCKED: HOW RELATIONAL CONTRACTING WITH SUPPLIERS CONSTRAINS GLOBAL BUYERS DURING AN ECONOMIC CRISIS
(with M. Taussig, B. Hong, K. Carlsson)
Advances in International Management (2017)
Abstract: This chapter is motivated by a surprising empirical finding: During the 2008 economic crisis, leading global buyers of labor-intensive manufacturing goods were more likely to terminate contracts with suppliers based in countries with strong formal contract enforcement institutions than with those in countries where such institutions were weak. We develop a formal model that explains this counter-intuitive finding as the result of heightened reliance on informal contracting when the formal contracting system is unreliable. This explanation contrasts with recent characterizations of outsourcing as an exercise of real options and adds to understanding of the effect of using relational contracting across multiple borders.
Keywords: Contracting systems; relational contracting; economic crisis
Suggested Citation: Wolfolds, S., Taussig, M., Hong, B., Carlsson, K. (2017). Tied up and Shocked: How Relational Contracting With Suppliers Constrains Global Buyers During an Economic Crisis. In T. Pedersen, T. M. Devinney, L. Tihanyi, & A. Camuffo (Eds.), Breaking up the Global Value Chain (Advances in International Management) (vol. 30, pp. 157-188). Bingley, UK: Emerald Publishing Limited.